Requirement Engineering
개요
- System services
- Constraints
Requirement = 시스템 서비스(System service) + 제약사항 (Constraint)
- System service = Functional requirements
- Constraint = Non-Functional requirements
RE process
- Development process에 따라서 빈도/시점 등은 달라질 수 있음
ex)
- Waterfall : 초반에 가능한 많은 Requirement를 정의
- Incremental : 초반에 가능한 많은 Requirement 정의 후 개발은 쪼개서 진행 (Release 1,2,3 등)
- Spiral : risk analysis, requirement 도출을 점진적으로 계속 진행
- Agile : 수시로 Requirement 도출
- RUP - 일반적인 Requirement process를 따서 만든게 RE Process
- 다음 단계로 진행
1. Feasibility Study (타당성 검토/분석)
> 개발 할지 말지를 조사
(조직의 목적에 부합할지, 예산안에 들어가는지, 사용중인 시스템과 integration 가능한지?)
2. Requirements Elicitation (요구사항 도출) & Analysis
> 다음 요구사항 도출
. Application domain, services 도출
. Constranint 도출
* 이해당사자(Stakeholder)관여 해야함
> 주요 Activity
. Requirements discovery
. Requirements classification and organization
. prioritization and negotiation
. Requirements documentation
3. Requirement Specification (요구사항 명세)
> 국제표준 이용
- Requirement Validation (요구사항 검증)
> 다음 방식으로 검증
. Validity
. Consistency
. Completeness - 기능들이 모두 적용
. Realism - 주어진 예산과 기술적으로 구현가능한지
. Verifiability - check가능한지
4. Requirement Document (문서화)
5. Change Management (지속적으로 진행)
> 요구사항 변경 관리
. Change Specification
. Change analysis and costing
. Change implementation
> 추적성이 중요함
. 소스 <-> Requirement <-> Desing <-> Code

1. Feasibility Study
목적
- 가능한지 여부를 확인해야 함
- 대안이 존재하는지? (alternative solution)
- Management group에 충분한 정보를 제공
- GO/STOP Decision
Feasibility Study 내용
- 기존시스템은 이러하다
- 문제는 뭐고
- 목표와 제한사항은 뭐다
- 가능한 대안은 뭐고
- 장/단점은 뭐다
Type of Feasibility
- Technical Feasibility
- 현재 기술로 가능한지? - Economical Feasibility
- Resource constraint 상으로 가능한지? - Schedule Feadibility
- 가용한 시간 내 가능할지 / Delay시 어떤 문제? - Operational Feasibility
- 사용될 수 있는지? (규제 등 포함)
* 신규시스템 개발 vs 대안들과 비교 -> Feasibility Analysis Matrix
. 4가지 측면 (Type of feasibility)에서 확인
2. Requirements Elicitation * Negotitation & Analysis
2-1. Requirements Elicitation (요구사항 도출)
- 해결해야 할 Problem 파악
- Problem 파악을 위해서 다음을 파악 해야 함
- 문제의 Boundary
- 문제의 배경 (어떤 조건 등)
- 누구의 문제인지? (Stakeholders)
- 왜 해결되어야 하는지? (달성하고자 하는 목표)
- 시스템이 어떻게 도움이 될런지? (시나리오)
- 언제까지 해결되어야 하는지? (Development constraint)
- 문제 해결에 방해가 되는 위험요소는 ? - 문제가 뭔지를 모름 (어려움이 있다)
- Stakeholders don't know what they really want
- 그들의 언어로 설명하다보니 문제의 명확성이 떨어짐
- Requirement의 Conflict
- 새로운 Stakeholder or Bisiness 환경의 변경 발생
=> Requirement 는 계속 변경되어 어려움 - 이해당사자 (Stakeholder)
- 시스템과 관련된 사람들 - Activity (Spiral / Iterative 하게 진행 해야 함)
- Requirement Discovery
- Requirement Classification & Organization
- Prioritization & Negotiation
- Rqquirement Documentation
요구사항 도출 시 기억해야할 원리들
1. Don't lose sight of the goal
- 좋은 품질의 시스템을 만들고, 이해당자자들의 합의가 있어야 함
2. 누가 똑똑한지 ?
- Stakeholder가 Smarkt하다는 것을 느끼도록 해야 해
- 문제 제기시에 충분히 잘 설명할 수 있도록 분위기 조성 해줘야해
3. 이해당사자는 요구사항이 다 달라
- 여러그룹의 이해당사자들이 모든 이해당사자를 대변하지 못함
4. 적절한 방법을 사용해야 해
- Interview
> Avoid "Why..?"
> Ask open-ended questions
- Role Playing
> from the viewpoint of the roles
- Brainstorming
> 중요한 Rule = 목적을 분명히 / 가능한 많은 아이디어 / 논쟁을 하지 말고
> 가능한 많은 아이디어를 모아야 함
> 아이디어는 자세히 명세할 필요 없음 (평가하지말고, 이름붙이지 말고, 논쟁하지 말고..)
- Requirement Workshop
> 이해관계자들 모두 모여
> Create consensus on the scope, risk and key feature
> Results immediately available
- Prototyping
> Demonstrate some or all of the externally observable behaviors
- Survey
- Use Case
- Questionnaires
> 통계적 분석이 가능 -> 인터뷰를 대체하지는 못함
> 질문Set이 준비 되어 있어야 함 / 문구 등을 잘 만들어야 해
- Storyboard
> Player, actor가 누구인지 구분해서 시나리오 식으로 진행
> 직관적으로 이해 가능
> 팀 리뷰에 좋아
- Review Customer Requirement Specifications
> Ask customers directly
5. 요구사항 변경을 받아들여라
- 불가피함
- 더 많이 보여줄 수록 더 많은 요구사항 발생
6. 도출된 요구사항은 잘 관리해라
- Record 필요 = Reason(이유), Assumptions(가정사항)
- Annotatied requirement lists -> ID 붙이는게 좋아
Elicted Requirement는 어떻게 해야 하나?
- 리스트로 관리
- Priority 분류
2-2. Requirement Negotiation
필요성
- . 서로간의 원하는 목표 등이 충돌 -> 조율
Negotitation Principles
- Use 4-step
- 문제와 사람을 분리하라
- 지위가 아닌 관심사에 집중해라
- 상호 윈윈을 위한 대안이 무엇인지 개발해라
- 객관적인 기준(데이터 등)으로 주장이 필요하다 - WinWin Approach
- Key concepts
> Win conditon - 이해당사자들 별 목표치
> Issue - 같이 만족시킬 수 없을 때
> Option - Issue를 해결할 수 있는 방법
> Agreement - Option에 대한 합의
- WinWin Equilibrium State 가 되도록 해야 함
- Step
> Success-critical stakeholder 확인
> Win Condition 나열
> 이슈 도출
> Top-level부터 win-win agreement의 협상 시작
> Spec에 기술하고 Plan 작성
> Project 완료될때까지 반복 해야 함
2-3. Requirement Analysis
Requirement Modeling 이란
- 잘 이해하는데 도움을 줌
- Guide elicitation
- 단계의 측정을 제공
- Uncover problem에 도움
- Understanding을 체크하는데 도움 - Good requirement model
- Complete
- Consistency
- Testability
Requirement Modeling Notation
- 자연어로 기술
- 표현의 자유로움
- 요구사항 간의 관계를 확인하기 어려움 (모호성) - Semi-formal notation
- UML - Formal notation
- Very detailed model
- 자동분석 가능
Principles for Modeling Notations
- 구현과는 독립적
- Abstraction (적절한 수준의 추상화가 필요)
- 의미가 분명해야 함
- Constructability 지원 해야 해 (부분 부분으로 모델링 후 합치는, 계층구조 지원)
- 분석이 쉬워야함
- 모델링을 통해서 reference가 쉬워짐 - link가 자유로워야함 (Traceability)
- 수행을 해볼 수 있어야 함
- Redundancy 없도록 (Minimality)
The State-of-the-Art Requirements Modeling Method
- Structured analysys
- Top-down Divide and conquer (쪼개가면서 사용)
- DFD (Data Flow Diagram)
- 기능적으로 분리하여 표현 - STD (State Transition Diagram)
- 상태 중심으로 표현 (동적 Behavior 등이 분명해 짐) - ERD (Entity-Relation Diagram)
- Data layout 중심
- Use case analysis
- Actor와 System간의 Use-case를 표현
- Use Case = Use Case Diagram + Texture
- Goal and Scenario based analysys
- 목표와 시나리오 기반으로 분석하는 모델링 기법
- Goal -> Scenario 형태로 발전 시킴
예> Goal = 유비쿼터스 기술이 접목된 ATM 서비스 제공한다
Scenario = 사용자는 ATM으로부터 현금을 인출한다 - 초기 목표를 가지고 Goal tree 생성
- 시나리오 수준으로 Refine 시킴
- Business layer -> Service layer -> Interaction layer -> Internal layer 로 나눠서 모델링 진행
Requirement Prioritization
- Implement 대상 선택 필요
- Time-to-market
- Next release
> 고려/분류 사항 = 중요성 , 비용은, 위험성 - 우선순위 매길 때 사용하는 방법
- ROI (Return on Investment)
> Cost vs Value (Compute the cost-value trade-off)
> Two approach
= Absolute scale
= Relative values -> Sorting 문제로 회귀 가능

- Estimation이 어려움
- AHP (Analytic Hierachy Process)
- Requirement 별 상대적인 Value를 구하고 Normalize 해서 구하는 방식
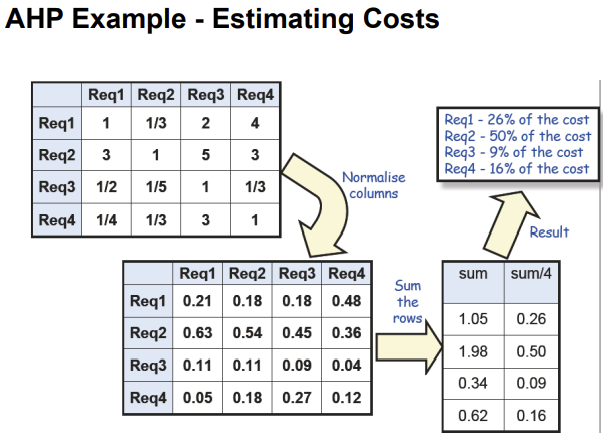
Priority 결정할 때 고려사항
- 주요 Factor를 찾아야 함
- 안전/보안이 중요한 경우 사용용이성보다는 안전/보안을 선택
- 사용자 고객만족이 우선인 경우
- PJT별로 Stakeholer 별로 다를 수 있음 - 우선순위 매길 때 주요한 Stakeholder는 포함해서 진행 해야 함
- 첫번째 Release 에 포함될 사항을 결정해야 함
- Stakeholder들 중에서 더 영향력이 있는 멤버의 내용을 우선시 함
Reruiement Prioritization Method
- Ranking
- Numerical Assignment (Grouping)
- Critical Priority, Moderate Priority, Optional Priority 로 분류해서 Assign - SoSCoW Technique
- MUST (Mandatory)
- SHOULD (High priority)
- COULD (Preferred but not necessary)
- WOULD (Can be postponeed and suggested for future execution) - Bubble Sort Technique
- 두개 간 비교 -> 연속으로 진행해서 Sorting - Hundred Dollar Method
- 각자 100달러를 가지고 각 Requirement에 배팅하여 결정
- 총합을 계산해서 Ranking 매기는 방법 - Five Whys
- Requirement가 중요한 이유를 5번까지 질문을 해서 진짜 중요한지 여부를 추출하는 방법
Requirement 분류
- List로 관리해야 함
- 관련된 정보들을 모두 넣어야 함
- 예) 다음과 같은 질문에 대한 답
> Requirement가 몇 개 인가요?
> High Priority는 어떤 것이 있나요?
> 이번 릴리즈에서 몇 % 적용 되었는지? - 주석(Annotation)을 잘 달아두어야 함 (Cost, 상대적인 우선순위 등)
- Effect & Cost
- 몇 번째 Release에서 적용할지
- Duration
- Technical risk - 선별을 해야 하는 것을 잊지마라
- Requirement 분류 시에 주요 그룹(이해관계자)이 참여해야 함 (Key group/stakeholder)
- 결과로 "An annotated list of requirement" 작성 (in agreement)
3. Requirement Specification
Requirements
- Type of Requirement
- User requirement
> 자연어 / 고객향
> Defined (정의된 수준)
- System requirement
> 좀더 구체적으로 명세화한 내용
> Specified (명세 수준) - Functional vs Non-Functional Requirement
- Functional
> 기능과 관련된 요구사항
- Non-Functional
> Timing Constraint
> 개발 표준 및 표준
> Challenge
. 모델링 하기가 어려움
. 정확하게 표현하기 어려움 (모순/상충되는 부분도 나타나게 됨)
. Measure하기 어려울 수 있음 (10만 Request 충족 해야 함) -> 측정 가능한 형태로 명세 되어야 함
> Quality Attributes (품질 속성) or Quality Requirement (품질 요구사항) 라고 부르기도 함
> 기능요구사항 보다 더 중요한 경우가 존재 (예. 성능 3초 이내 -> 충족하지 못하면 사용하지 않는 시스템)
> Critical System인 경우 비기능 요구사항을 주요 기능요구사항으로 포함시키기도 함
(Safety, Security 요구사항 등)
> Three Type
. Product requirement = Reliability, Performance 등
. Organizational requirements = 조직의 기준, 정책, 구현언어(방법/플랫폼) 등
. External requirements = 법제도, 윤리적인 사항
> 처음부터 도출이 어려운 경우 Goal을 먼저 도출 한 후에 발전 시키는 방법이 있음
- Domain requirement
> 특정 Domain의 특성을 반영한 요구사항
> 꼭 만족되어야 하는 경우가 많음
Requirement Completeness and COnsistency
- Complete = 요구되는 기능이 모두 포함되어야 함
- Consistent = 서로간에 Conflict가 되지 않아야 함
- 자연어로 표현 시 Complete & Consistent가 100% 달성되기는 불가능함
- Requriement model을 사용할 필요가 있음
4. Software Requirement Document
Software Requirement Document
- SRS (Software Requirement Specification) or SRD (Software Requirement Document)
- 사용자 요구사항에 대한 공식적인 문서
- WHAT에 집중해야 함 -> 설계이슈가 포함되지 않도록 권고함
- User requirement + System requirement 기술되도록 포함해야 함
- Design document가 아님 - 목표 = 주어진 시간 내에 가장 좋은(최선의) 품질의 Product을 생성하기 위함
Purposes of SRS
- Communication 용도로 사용
- Purpose
- Communication
- Contractual
- Baseline for evaluating the software = Test 및 평가의 기준이 되기도 함
- Baseline for change control
Feature for Good Specifications
- Valid (Correct)
- Unambiguous
- Complete = Conceptual completeness + Structual completeness
- Understanable (Clear)
- Consistent = 용어정리가 우선 필요
- Ranked
- Verifiable
- Modifiable = Cross-referencing (연관된 요구사항은 Reference가 잘 되어 있어야 함)
- Traceable = 무슨 근거로 왔는지 알아야 함 / ID 부여하면 관리 좋음
SRS Contents
- Include
- Functionality
- External interface
- Required performance
- Quality attribute
- Disgn constraints - Not Include
- Project development plan = SRS와 PJT는 Life-time 범위가 다름
- Product assurance plan (Test plan, Qaulity assurance 등은 별도 문서로 작성 필요)
- Design - Mistake
- 불필요 정보 포함
- Over-specification
- 모순/모호한 내용
- 뒤에서 설명될 내용을 앞에서 표현하는 경우
- 희망사항 포함
- 사용자에 대한 제약사항 = 바람직하지 않음 (예. User가 이렇게 사용해야 한다)
- 중요한 내용이 여기저기 흩어져 있는 경우 (Jigsaw Puzzles)
- 불필요하게 새로운 단어 만들어서 사용하는 경우
- 일관된 Terminology term 사용해야 함
- 행간 의미 읽어서 파악하도록 표현
Requirement & Design
- 원칙적으로
- Requirements should state WHAT THE SYSTEM SHOULD DO
- Design sould describe HOW IT DOES THIS
Structured Specifications
- Problems of SRS in Natural Language 존재함
- Lack of clarity
- Requirement confusion
- Requirement amalgamation
- 이를 해결하기 위해서 Structured Specification 사용
- Form-based specification
- Form base의 Template을 제공해서 거기에 맞춰서 작성하도록 유도
- Function, Description, Inputs, Source, Output, Action, Requirements, Pre-condition, Side effect 등 - Tabular specification
- Condition / Action을 Table 형태로 표시
- Form-based specification
- (참고) 공공SW사업 제안요청서 작성을 위한 요구사항 상세화 실무가이드라인
매뉴얼ㆍ가이드라인 및 기타 | SWIT 소프트웨어산업정보시스템
www.swit.or.kr
'Software Architect' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Software Architecture] 아키텍처 설계 (0) | 2022.04.05 |
|---|---|
| [Software Architecture] Requirement Engineering - 2 (0) | 2022.04.01 |
| [Software Architecture] SA Framework (0) | 2022.03.31 |
| [Software Architecture] Architecture Decisions (0) | 2022.03.29 |
| [Software Architecture] RUP (0) | 2022.03.29 |

