Flyweight Pattern
개요
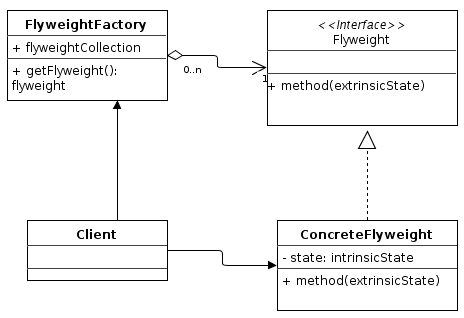
- 동일/유사한 객체들 사이에 가능한 많은 데이터를 서로 공유하여 사용하도록 하여
메모리 사용량을 최소화 하는 패턴
[참고] 메모리를 절약하는 방법
1. 생성 시 자주 사용하는 부분을 떼어내어 공용 객체로 생성
2. 한번 생성한 객체는 다시 사용하지 않도록 저장 후 활용하는 방법 -> Flyweight Pattern
구현 방법
import java.util.HashMap;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Factory fac = new Factory();
Tree[] trees = new Tree[100];
for (int i = 0; i < trees.length; i++) { // [1]
trees[i] = new Tree(i % 7, i, 100, fac.makeTreeInfo("소나무", "##IOFNQ$!"));
}
trees[34].show();
}
}
class Factory { // [2] 공통되는 부분
HashMap<String, TreeInfo> map = new HashMap<String, TreeInfo>();
TreeInfo makeTreeInfo(String name, String texture) {
String key = name + "|" + texture;
if (!map.containsKey(key)) { // [3]
System.out.println("Info 생성!");
map.put(key, new TreeInfo(name, texture));
}
return map.get(key);
}
}
class Tree { // [4]
private int y, x, hp;
TreeInfo info;
public Tree(int y, int x, int hp, TreeInfo info) {
this.y = y;
this.x = x;
this.hp = hp;
this.info = info;
}
public void show() {
System.out.println("Y:" + y);
System.out.println("X:" + x);
System.out.println("HP:" + hp);
System.out.println("name:" + info.getName());
System.out.println("texture:" + info.getTexture());
}
}
class TreeInfo {
private String name;
private String texture;
TreeInfo(String name, String texture) {
this.name = name;
this.texture = texture;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getTexture() {
return texture;
}
}- [1] 여러개의 Tree를 만드는 경우
> X, Y, HP (위치) 는 각 Tree마다 다름
> Name, Texture 는 각 Tree마다 공통적인 부분 - [2] 공통되는 부분을 Factory를 통해서 먼저 만듦
> 여러개 안만들어 지도록 HashMap을 통해서 TreeInfo를 관리함 - [3] HashMap에서 기존에 등록된 TreeInfo가 아닌 경우에만 새로 생성함
- [4] 개개의 나무를 설정하는 부분
'Software Architect' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Software Architecture] SW 공학 (0) | 2022.03.28 |
|---|---|
| [Design Pattern] Command / Strategy / State Pattern (0) | 2022.03.25 |
| [Design Pattern] Observer Pattern (0) | 2022.03.25 |
| [Design Pattern] Decorator Pattern (0) | 2022.03.24 |
| [Design Pattern] Adapter Pattern (0) | 2022.03.24 |



