Command Pattern
개요
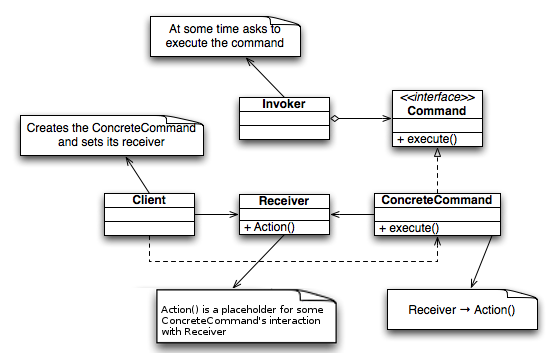
- 요청을 객체의 형태로 캡슐화하여 사용자가 보낸 요청을 나중에 이용할 수 있도록 매서드 이름, 매개변수 등 요청에 필요한 정보를 저장 또는 로깅, 취소할 수 있게 하는 패턴
- 커맨드를 수행할 수 있도록 하는 패턴
구현 방법
public class main {
public static void show(Box box) {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
if (box.getX() == i) System.out.print("#");
else System.out.print("_");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
Box box = new Box();
Command cmdRight = new Right(box);
Command cmdLeft = new Left (box);
while (true) {
System.out.print("\nInput Command : ");
String cmd = sc.next();
if (cmd.equals("left" )) cmdLeft .run();
if (cmd.equals("right")) cmdRight.run();
show(box);
}
}
}
class Box {
private int x = 5;
public int getX() {
return x;
}
public void setX(int x) {
this.x = x;
}
}
interface Command {
void run();
}
class Left implements Command {
Box box;
public Left(Box box) {
this.box = box;
}
@Override
public void run() {
box.setX(box.getX()-1);
}
}
class Right implements Command {
Box box;
public Right(Box box) {
this.box = box;
}
@Override
public void run() {
box.setX(box.getX()+1);
}
}- Command를 Class로 만들어서 사용
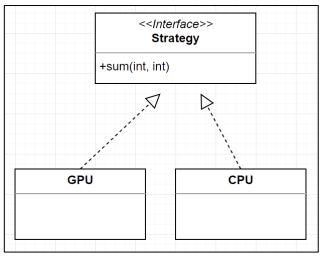
Strategy Pattern
개요
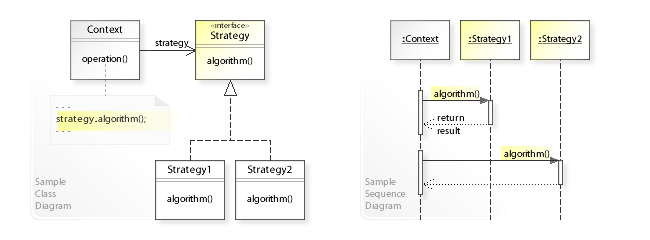
- 실행 중에 알고리즘을 선택할 수 있는 행위 디자인 패턴
구현 방법
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Strategy st = null;
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Input two num ?");
int a = sc.nextInt();
int b = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Algorithm : ");
System.out.println("1. Using GPU");
System.out.println("2. Using CPU");
int n = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Results =========");
if (n==1) st = new GPU();
if (n==2) st = new CPU();
int c = st.sum(a, b);
System.out.println(c);
}
}
interface Strategy {
int sum(int a, int b);
}
class CPU implements Strategy {
@Override
public int sum(int a, int b) {
// CPU Algorithm
return a+b;
}
}
class GPU implements Strategy {
@Override
public int sum(int a, int b) {
// CPU Algorithm
return a+b;
}
}
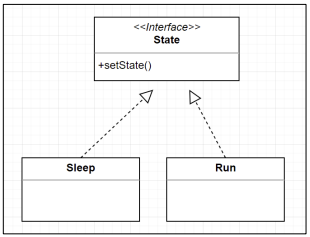
State Pattern
개요
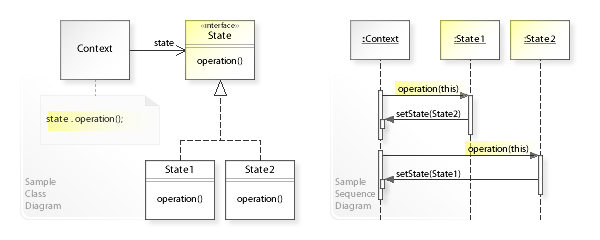
- 상태값을 저장하는 패턴 -> State Machine 개발시 이용
구현 방법
public class main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Arbiter stateMachine = new Arbiter(new IdleState());
for (int i = 0; i< 10; i++) {
stateMachine.runState();
}
}
}
class Arbiter { // [1]
State nextState;
Arbiter(State startState) {
nextState = startState;
}
public void setState(State state) {
nextState = state;
}
void runState () {
nextState.run(this);
}
}
interface State { // [2]
void run(Arbiter arbiter);
}
class IdleState implements State { // [3]
@Override
public void run(Arbiter arbiter) {
System.out.println("[IDLE] Waiting");
System.out.println("[IDLE] Send condition");
send(arbiter);
}
private void send(Arbiter arbiter) {
System.out.println("[IDLE] Prepare Send");
arbiter.nextState = new SendState();
}
}
class SendState implements State {
@Override
public void run(Arbiter arbiter) {
System.out.println("[SEND] Sending");
System.out.println("[SEND] Sending complete");
arbiter.nextState = new FinishState();
}
}
class FinishState implements State {
@Override
public void run(Arbiter arbiter) {
System.out.println("[FINISH] Finishing");
System.out.println("[FINISH] Finishing complete");
arbiter.nextState = new IdleState();
}
}- [1] State 관리 객체 -> 실제로 실행 시켜 주는 역할 / nextState가 어떤 것인지를 지정
- [2] 상태 저장용 interface
- [3] 상태 클래스
: run method -> 상태가 변경되었을 때 수행해야 하는 부분
패턴 비교
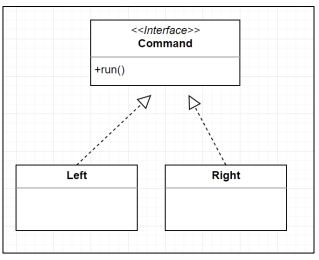
Command / State / Strategy Pattern 비교
| Command Pattern | Strategy Pattern | State Pattern |
| Command를 객체로 생성 | 적용할 알고리즘을 객체로 생성 | 각각의 상태를 객체로 생성 |
 |
 |
 |
'Software Architect' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Sofrware Architecture] SA 개요 (0) | 2022.03.28 |
|---|---|
| [Software Architecture] SW 공학 (0) | 2022.03.28 |
| [Design Pattern] Flyweight pattern (0) | 2022.03.25 |
| [Design Pattern] Observer Pattern (0) | 2022.03.25 |
| [Design Pattern] Decorator Pattern (0) | 2022.03.24 |


