In-Memory computing의 기반이 되는 기술에 대해서 알아보면 다음과 같다.
Types of Queries
- OLAT & OLTP
| Category | OLTP (Online Transactional Processing) | OLAT (Online Analytical Processing) |
| Applications | Manage usual business, operational and management applications | Management system, reporing and decision |
| Effectiveness | Number of transactions per sec | Response time per query |
| Volume | Large number of short oline trancation (INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE) |
Low volume of complex analysical transaction (SELECT) |
| Space | Operational data stored, typically small | |
| Data Source | Operational information of the application | Historical and archive data |
| Focus | Updating Data | Retrieval of information |
| Uers | Common staff | Managers and Executives |
- Database는 OLAP와 OLTP 모두를 좋은 성능으로 처리할 수 있어야 하지만 대부분의 시스템에서는 가능하지 못함
- Columnar storage가 OLAP 쿼리의 처리를 향상시키고 OLTP workload를 위해서 in-memory row storage가 높은 성능을 보장함
- 복합 부하((Mixed workload)를 처리하기 위해서 MVCC와 2단계 commit으로 최적화 된 Logging schema로 Reduced Locking이 적용됨
- DB의 모든 Read가 Transaction의 일관된 뷰를 구성하는 모든 정보를 포함하는 transaction token에 의해 보장되는 일관된 스냅샷을 갖게 됨
- 2단계 commit을 최적화 하기 위해 첫번째 commit 이후에 log를 disk에 쓰고 두번째 commit은 비동기적으로 쓰여지게 됨
Changing in Hardware

- Disk writing and reading이 병목구간
- CPU speed and RAM cpaity was not the same as disks
Encoding
- Dictionary encoding
- DB 병목구간을 줄이기 위해서 data access time을 줄이는 노력 -> 압축 -> Dictionary 활용
- 각 테이블의 컬럼 별
dictionary + attribute vector (hash table과 비슷) with valueID - 많은 중복 데이터가 있는 경우에 특히 효율적
- Search 처리 프로세스
- 요청 값을 Dictionary에서 search하여 해당되는 ValueID 찾음
- Attribute를 ValueID로 Scan
- Search result에서 ValueID를 해당되는 dictionary value로 replace
- Encoding 후에 dictionary의 정렬을 통해서 access time을 줄일 수 있음
- Sorted dictionaries의 lookup speed = O(long(n)) with binary search
- 하지만 dictionary에 존재하지않는 새로운 데이터의 입력은 dictionary의 re-sort 및 attribute vector의 update를 야기하여 Cost가 많이 소요됨
- Compression
- Memory는 여전히 제약이 있는 Resource로 cost를 줄이는 노력이 필요
- 이를 위해서 dictionary 적용 + 추가 compress 수행
- 압축기술은 가벼워야 하며 그렇지 않은 경우 encoding/decoding의 cost가 더 비싸짐
- 주로 사용되는 Compressiong 기술
- Prefix Encoding - 특정 컬럼이 동일한 값의 long sequence를 가질 때 사용
- Run-length Encoding - Cardinality가 낮고 발생 빈도가 낮은 경우에 사용
- Cluster Encoding - Attribute vector가 동일 크기의 여러개의 cluster로 나눠질때 사용
(Cluster가 동일한 값을 가질 경우에 one value로 압축) - Sparse Encoding - 많은 empty, null값을 가진 경우
- Indirect Encoding - Cluster encoding과 비슷, 특정 컬럼에 의해 정렬된 table에서 많이 사용되며 각 컬럼들간에 상호관계가 존재함. 각 cluster별 각각의 dictionary 이용
- Memory는 여전히 제약이 있는 Resource로 cost를 줄이는 노력이 필요
Data Layout
- RDB가 2차원인 경우 in-memory에 모든 데이터는 1 차원 방식으로 저장 되어야 함
- DB storage layer는 column, Row 또는 Hybrid layout를 결정해야 함
- 하지만 다양한 workload에 의해서 각 layout 별로 장점이 있을 수 있음
- Hybrid는 각 장점을 모두 가짐
| Row Data Layout | Comumn Data Layout |
| Data stored in tuples | Data sotre attribute-wise |
| Low cost for reconstruction, but higher cost for scanning a single attribute | High cost for reconstruction |
| Lower compression techniques | Higher compression techniqueues |
| Fast scan of a single complete tuple or joint of complete tuples | Fast column scanns or joint of |

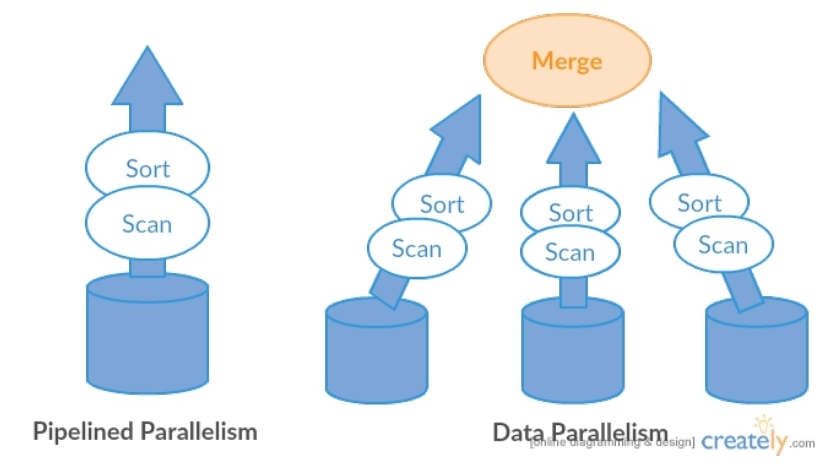
Parallelism
- Query processing의 속도를 높이기 위해서 우리 데이터와 프로세스에 대한 병렬화가 적용됨
- 2가지 종류의 병렬 방식 존재
- Pipeline parallelism = 뒤따르는 operation이 이전 operation 완료전 수행 가능
- Data parallelism = 데이터를 나눠서 각기 처리 후 Merge는 방식
Data Aging and Archiving
- 모든 데이터가 시스템에서 사용되지는 않음
- 현재 데이터보다 10년 전 데이터의 사용 빈도는 낮을 것임
- 하지만 이전 데이터도 분석 쿼리를 위해서 사용될 수 있으므로 삭제는 불가함
- 이를 위해서 aging 기법을 사용할 수 있음
- Hot / Cold 데이터를 다른 곳에 저장하지만 data schema 변경은 없으로 cold 데이터도 여전히 access 가능
Database Operations
- Insert, Delete and Update
- Columnar layout과 dictionary encoding으로 인해 DML문도 다음과 같이 변경됨
- Insert
- Row organization - Tuple이 table의 가장 마지막에 추가됨
- Columnar organization - 각 column에 새로운 entry가 추가됨
- 새로운 entry가 추가되면 새로운 dictionary 값의 변경이 필요한지 여부를 확인하고
- 변경이 필요하지 않은 경우에는 새로운 entry를 dictionary에 추가하고 ValueID가 attribute Vector에 추가됨
- 변경이 필요한 경우에는 dictionary에 새로운 entry를 추가한 후에 재정렬을 수행하고 attribute를 재구성하게 됨 -> 굉장히 expensive함
- Update
- Update 수행은 동일하게 수행되며 문제는 Single value의 update에 소요되는 비용
- 일반적인 수행 단계 = Update dictionary -> Reorg Dictionary -> Reorg Attribute vector -> Update all old values in th attribute vector
- 이러한 성가스러움을 피하기 위해서 Insert-only approach 사용
- Delete
- Physicl delete - tuple이 DB에서 완전히 제거되는 것
- Logical delete - Validity of a tuple is terminated -> 삭제 flag를 이용
- Insert-only approach
- 데이터 변경에서 invalidate tuple을 통해서 update / delete를 구현 가능
- 시간별로 데이터가 어떻게 변경되었는지 확인 가능 (for Historicl analysis)
- Dictionary의 clearing 없이 수행 가능
- Select
- Relational Algebra에서 데이터 추출을 위해 구현
- 효율적인 Plan을 가지기 위서 대부분의 Selective queries가 도출되고 가장 작은 Set이 먼저 선택 되어야 함
- 예를들어
낮은 cardinality를 가지는 컬럼이 있는 경우 이것은 첫번째로 선택되어야 함
Dictionary에서의 lookup은 한번 수행되고 모든 비교는 dictionary의 encoded value와 수행 - 만약 Query에서 전체 tuple을 가져오는 것이 목적이라면 row oriented schema가 효율적이고 동일한 attribute를 가진 여러 row를 가지는 것을 목적으로 한다면 column-oriented가 제안된다
- 예를들어
- 테이블의 적절한 분석을 통해서 row 또는 column orginization이 결정됨
- 따라서 이를 결정하는 것이 전체 성능차원에서 중요한 요인임
| Row Store | Column Store | |
| Simple SELECT query | ~46 ms | ~93 ms |
| Complex SELECT query | 1.57 sec | ~ 127ms |
Workload Management and scheduling
- 시스템에서 수행되는 많은 부하 중에는 응답시간이 중요한 부하와 그렇지 않은 부하가 포함됨
- transactional application have critical business processes intercation with customer
- OLAP queries nomally are not that time sensitive, and a fast response is not always needed
- Query는 Service level objective를 가지도록 함 -> Dynamic, Simple scheduling
- 주요 목표는 transaction query를 손상없이 Commit 된 모든 트랜잭션 쿼리를 보장하며 처리 쿼리 수를 최대화 하고 분석 쿼리의 응답시간을 최소화하는 것임
- 중요한 것은 분석 쿼리는 DB에서 수행되면 더이상 관리(stop or pause)가 어렵다는 것임
- 이것은 Peak 시간대의 전체 시스테을 멈출 수 있고 어떤 것으로도 해결할 수 없게 만듦
- 시스템 안정성과 가장 중요한 쿼리 전달을 보장하기 위한 가설은 OLTP 쿼리에 많은 리소스를 할당하여 Throughput Goal을 보장하는 것
- OLAP 쿼리와 같은 긴 쿼리를 예측할 때 높은 overhead가 발생 함
- OLTP가 충분한 리소스를 할당받은 후에 남은 리소스가 분석 쿼리에 할당 되는 것이 효율적임
In-Memory Capabilities
- 요약하면 5가지 주요 기술 특징
- Data stored in memory - decrease access time
- Multiple CPU acn process multiple requests at the same time, taking full advantage of computer resources - parallelism
- Handling mixed workloads, OLAP and OLTP, on the same platform
- High compression techniques, through the column oriented organization
- Insert-only approach
'Database' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [HANA] Column store index (0) | 2019.04.22 |
|---|---|
| [HANA] In-Memory Computing 기본-2 (0) | 2019.04.21 |
| [HANA] Calculation View (0) | 2019.04.20 |
| [HANA] Indexserver와 SQL Execution (0) | 2019.04.19 |
| [HANA] SQL Statement Collector (0) | 2019.04.18 |
